A proxy server act as a gateway between you and the Internet. An intermediate server separates end users from the websites they browse. Proxies provide different functionality, security, and privacy levels depending on your use case, needs, or company policy. If you use a proxy server, the Internet traffic passes through it on the way to URL you requested. The request then goes back through the same proxy server. Then, the server sends you the data from the site. Modern proxies do much more than just forward web requests. They can feature data security and network performance features as well.
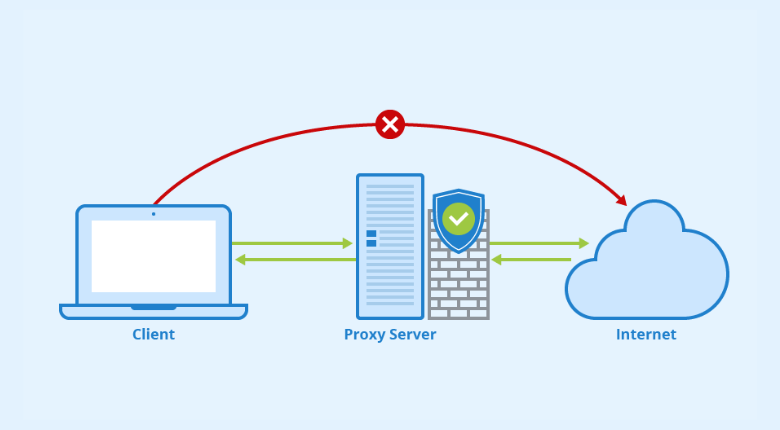
Simplified scheme of a proxy server mechanism
How Does a Proxy Server Work?
Every device on the Internet has a unique IP address (Internet Protocol address). Think of this IP address as the mail address of your computer. Just as mailman knows how to deliver mail properly, the Internet knows how deliver data to a proper recepient. A proxy is the same computer on the Internet, but with different configurations. It also has its IP address, and your computer knows it. When you send a web request, your request is first sent to a proxy. Then it makes a web request on your behalf, collects the response, and forwards it to your PC.
A proxy server can make changes to the data you send while forwarding your requests and still receive the information you expect to see. It can also change your IP address, so the web server doesn’t know exactly where you are. In addition, it can encrypt your data so it can’t be read in transit. Finally, a proxy server can block access to specific web pages based on your IP address.
Why is It Worth to Use a Proxy Server
Here are some reasons why organizations and individuals use a proxy server:
- To control internet usage of employees or children. It is common for organizations to set up proxy servers to control and monitor how their employees use the Internet. For example, most organizations do not want employees to browse certain work-hours websites (such as social networking sites). So they can set up a proxy to block access to such websites instead of redirecting you with a note asking you to refrain from browsing said sites on the company network. Likewise, they can track and log all web requests, so even if they don’t block the site, they know how much time you spend on social media at work. In the same way, parents can block children’s access to websites that children shouldn’t visit.
- Bandwidth savings and improved speeds. Using a good proxy server can improve overall network performance. Proxy servers can cache (save a copy of a Web site locally) popular Web sites, so when you request loaris.app, the proxy server checks to see if it has the most recent copy of the site and then sends you the saved copy. This means that when hundreds of people go to loaris.app from the same proxy simultaneously, the proxy sends only one request to loaris.app. This saves bandwidth for the company and thereby improves network performance.
- Improved security. Proxy servers provide security benefits. For example, you can set up a proxy server to encrypt your web requests so that outsiders cannot read your transactions. You can also deny access to known malicious sites through a proxy server. In addition, organizations can link their proxy server to a virtual private network (VPN) so that remote users can always access the Internet through the company’s proxy server. A VPN is a direct connection to a company’s network that companies provide to external or remote users. Using a VPN, the company can monitor and verify that their users have access to the resources they need (internal data, email) and provide a secure connection for the user to protect company data.
- Privacy benefits. In addition to the security benefits, individuals and organizations use proxy servers to browse the Internet more privately. For example, proxies change the IP address and other identifying information contained in a Web request. That way, the target server doesn’t know who made the original request, which helps keep your personal information more private.
- Get access to blocked content. Proxy servers allow users to bypass regional content restrictions companies or governments impose. Is Certain content not available in your region? Log in to a proxy on the other side of the country and watch from there. The proxy server makes it seem like you’re in California, but you live in North Carolina. Several governments around the world closely monitor and restrict access to the Internet, and proxies offer their citizens uncensored access to the Internet.
Now you know what a proxy server is and what it is used for. Now no less important information is the possible risks of using proxy servers. It is essential to be careful when choosing a proxy server. A few risks can completely negate all the potential benefits.
Proxy Server Risks
- Free proxy server risks: Using one of the many free proxy services can be risky, even for services that use ad-based revenue models. Usually, free means they are not particularly invested in server hardware or encryption. There are likely to be performance issues and potential data security problems. If you ever find a completely “free” proxy server, proceed cautiously. Some of them want to steal your credit card numbers.
- Browsing history log: The proxy server knows your original IP address and web request information, which may not be encrypted, or stored locally. Please check whether your proxy server logs and stores this data and what storage or law enforcement cooperation policies they follow. If your goal is to use a proxy server to provide privacy and the vendor logs and sells your data, perhaps you are not getting the expected value of the service.
- No encryption: If the proxy server does not use encryption, it is not recommended. No encryption means that you send your requests in plain text. Anyone who can intercept the traffic can easily get usernames, passwords, and account information. Make sure that any proxy you use provides full encryption capability.
Types of Proxy Servers
Proxy services can be different and have different tasks. Therefore, it is essential to understand exactly what the tasks of a proxy server are and to make sure that the proxy server is suitable for your tasks.
- Transparent Proxy. A transparent proxy tells websites it is a proxy, so it doesn’t hide your IP address, identifying you to the web server. Companies, public libraries, and schools often use transparent proxies to filter content: they are easy to set up on both the client and server sides.
- Anonymous Proxy. An anonymous proxy hides your real IP address. This helps prevent identity theft and keeps your online activities private. They can also contain a website that provides targeted marketing content based on your location. Anonymous browsing will prevent a website from using some advertising targeting techniques but is not a guarantee of complete protection.
- Distorting proxy. A distorting proxy server transmits a false IP address to you, identifying itself as a proxy. This serves the same purpose as an anonymous proxy. However, by sending a false IP address, you can appear to come from a different location to bypass content restrictions.
- High Anonymity proxy. Proxy servers with high anonymity periodically change the IP address they provide to the web server, making it very difficult to track traffic. Proxy servers with high anonymity, such as the TOR network, are the most private and secure way to read the Internet.
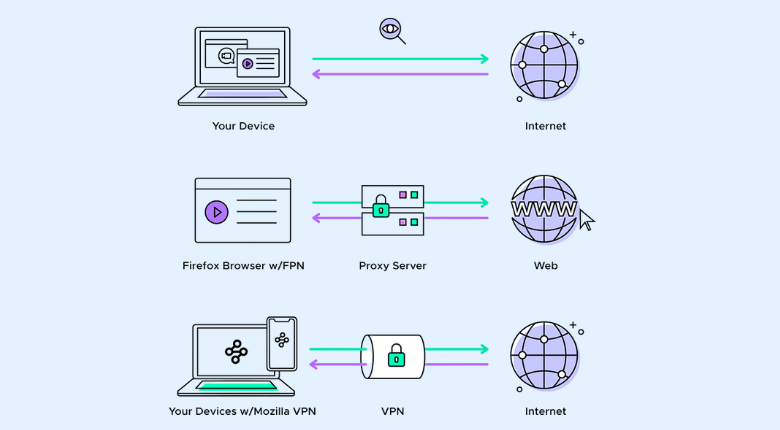
Difference VPN VS Proxy
VPN VS Proxy
At first glance, proxy servers and virtual private networks (VPNs) may seem interchangeable because they route requests and responses through an external server. Both also allow you to access blocked or inaccessible websites in your region or country. However, VPNs offer better protection against hackers because they encrypt all traffic.
In case you need constant access to the Internet to send and receive data that needs to be encrypted, or if your company needs to disclose data that you need to hide from hackers and corporate spies, a VPN will be the best choice. If an organization needs to allow its users to browse the Internet anonymously, a proxy server can help. It’s the best solution if you want to know what websites employees are using or want to ensure they have access to sites blocking users from your country.
A VPN is better suited for business because users usually need secure data transfers in both directions. Company information and personal data can be precious in the wrong hands, and a VPN can provide the encryption needed to protect it. On the other hand, a proxy may be an appropriate choice for personal use, where a breach will affect only one user. You can also combine both technologies, especially if you want to limit the number of websites users visit on your network and encrypt their communications.