You can use different proxy servers, VPNs, and Tor. This is useful when you need to change the IP address to access prohibited content in your region, or to hide your real location. Lets compare proxy vs VPN vs Tor, and figure out what is best to use for security purposes.
What Is a Proxy Server?
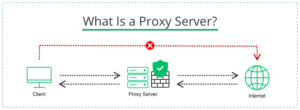
The user’s computer is connected to the website and the server can see information about your connection. Such as your IP address, the browser from which the connection is made, the plugins used (if they interact with the site), the operating system and its version. A Proxy connects you through a different server before accessing the website.
What Is a Proxy Server?
A proxy server is an intermediary between your browser and a website. It connects to the website on your behalf, like that friend who hands your notes to the cute girl in class. Proxy servers perform different functions depending on their type; some proxies can even swap your location with their own, allowing you to bypass geographic blocks and access site content only available in certain countries.
What is the Purpose of a Proxy Server?
The proxy server is designed for different applications. By using a proxy, network administrators can restrict access to specific resources. Proxies can also be used to cache popular sites, so downloading data from these resources is faster. You can save traffic because the proxy server can compress all requested content. This way different “turbo modes” in browsers work .
But it is worth noting that this feature has both positive and negative sides. So, the technology itself is not does not fit different connection types. This means that each type of Internet connection has its proxy server type. For example, FTP requires only FTP proxies. If you use HTTP, you must use HTTPS and HTTP proxy servers. These limitations require using a special type of SOCKS proxy server, which allows you to handle more traffic. But it doesn’t solve all problems, because it’s generally slower. It’s also worth noting that the proxy only works with traffic that passes through.
Proxy Security
Proxy servers do not encrypt traffic in any way, and all types of proxies have the same security issue. HTTPS is encrypted in a similar manner to a standard internet connection, using SSL encryption. The note analogy is a good way to imagine the size of the tragedy.
Trusting an intermediary 100% is like sending a love note with no envelope. The proxy server can see what is being sent through it, so you have to trust that the server will not reveal the contents of the note. Free proxy servers can have a bad reputation, so you have to be careful about which ones you use. It is like giving your envelope to the first person you see, which is not safe.
What Is a VPN (Virtual Private Network)?
What Is a VPN (Virtual Private Network)?
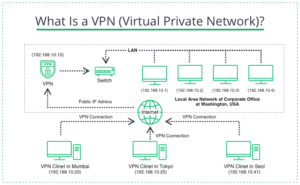
A VPN (Virtual Private Network) is a technology with a wider range of features and does not have as many drawbacks.The original purpose of a VPN was to connect computers remotely into a single network, but it then became a means of anonymizing traffic. A VPN works similar to a proxy, routing the traffic through an intermediate server before reaching the Internet.From one side, this allows access to blocked resources, but from the other side, the user keeps his anonymity. This happens because the website it visits believes the request did not come from a user’s IP address, but from the IP address of the VPN server.
📌 Related Content: An IP address, or Internet Protocol, is the rules responsible for routing data across networks and delivering it to the correct destination. IPv4 vs IPv6, what’s the difference?
VPN vs Proxy: What’s the Difference?
VPN and a Proxy: Differences in Pay Attention
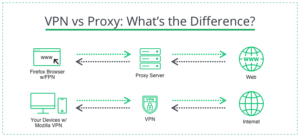
VPNs and proxy services differ in that VPNs provide end-to-end encryption of all data between the VPN server and the connected device. Turning it on creates a secure connection between the device and the VPN server, making all information inaccessible to potential hackers. On the other hand, the proxy has no end-to-end encryption. Records transmitted between the proxy server and the computer can be stolen at any time by a third party or by the device itself. VPNs encrypt all traffic from all programs, not just your browser activity, and can be installed on your device as a separate app. A proxy can only be installed on your browser and only works with web traffic.
VPN Security
The VPN is much safer than a proxy because it uses AES-256 and ChaCha20 (advanced encryption algorithms) to encrypt your connection and anonymize user traffic. But some VPNs have their negative nuances. For example, some have repeatedly been caught spying on user data. An example of such a service was Betternet VPN, which used more than 14 libraries to spy on users (over 38 million), and Service Hola, which did the same.
What Is Tor?
What Is Tor?
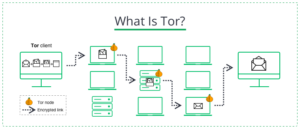
Tor is an anonymous network that uses so-called onion routing. The latter means that your data passes through several intermediary servers, called nodes, before reaching the Internet. The protection around the data is like the layers of the onion. Tor is similar to VPNs and proxies in that it anonymizes your traffic by passing it through other servers, but there are more nodes in the Tor network than other anonymization methods.
The first and second nodes see traffic only after three levels protect it. They remove these layers like the bulb’s skin, identifying the third node, which then gets into the center and connects to the Internet. Each node only knows the IP address of the node standing in front of it. Therefore, the source IP address will be lost when user traffic reaches the last host. Users themselves deploy nodes on their computers; hence more users are safer than the network.
Tor Security
Tor was based on Firefox and has been improved with additional settings that prevent sites from tracking users. In this way, the browser can distinguish all scripts on the site, prohibit user data collection, and force sites to use encryption. But all this sounds good, and there are its negative nuances.
- The use of Tor is not easy to track, which confuses law enforcement.
- The risk for the owners of the output nodes is very high, as they are responsible for the actions of users in the network.
- The owners of the exit nodes see all your traffic, which allows them to track everything indirectly. Law enforcement agencies use this nuance.
- The multilevel encryption of the Tor network is extending, which is why most sites refuse to work through the Tor browser.
- Tor, as well as a proxy, does not filter all system traffic.
Proxy vs VPN vs Tor
A VPN is the best way to protect your online security. Do not use unreliable VPN services; only use those with a good reputation. Find out more about a particular service on the Internet, in specific articles, regarding reliability. A VPN is a solution that focuses on speed and convenience and can cost money for its creators or charge a fee for its use. Proxy servers are another solution and are good for getting around big geo-blocks.
Tor focuses on giving anonymity at the expense of many nodes, while a VPN provides a secure, encrypted connection. A VPN is the best option in most cases because its connection is protected and speedy. Proxy servers and Tor don’t have that level of security, so your privacy and security can only be assumed. But to get the most out of it, the user can use a VPN and Tor simultaneously. Of course, connecting a VPN through Tor is much slower than a proxy but more reliable for user anonymity. As you can see, the comparison of Proxy vs VPN vs Tor heavily depends on users’ needs. Choose what’s best for you.
