In today’s digital landscape, organizations face increasing cyber threats. They can disrupt operations, compromise sensitive data, and damage reputations. Security Information and Event Management is a robust cybersecurity solution that helps organizations detect, respond to, and mitigate these threats. Today we will look at SIEM, explaining how it works, why it’s essential, and take a look at its features and capabilities.
What is SIEM?
Security Information and Event Management, aka SIEM – is a software solution that combines security information management (SIM) and security event management (SEM) functionalities. This provides comprehensive security monitoring, threat detection, and incident response capabilities. Organizations use SIEM to collect, analyze, and correlate security data from various sources in real time. As a result, it allows us to spot and respond to security incidents and threats.
Why is it important?
Since cyber threats constantly evolve, organizations face the challenge of promptly detecting and responding to sophisticated attacks. SIEM is crucial for identifying potential security incidents by analyzing security events and data from diverse sources. Among such sources are firewalls, intrusion detection systems, endpoints, applications, etc. As a result, SIEM helps organizations gain visibility into their IT environment. This helps with early threat detection and proactive responces, prevention and damage mitigation from security incidents.
How does it work?
In short, SIEM works through a multi-step process:
- Collects data from various sources, such as logs from servers, network devices, and applications, as well as other security tools like firewalls, antivirus, and intrusion detection systems.
- Normalizes the collected data by converting it into a standard format. It makes it easier to analyze and correlate events across different sources.
- Uses advanced analytics and rule-based algorithms to correlate events from different sources in real time, identifying patterns and anomalies that may indicate potential security incidents.
- Compares correlated events against predefined rules, policies, and intelligence feeds to identify known threats and potential zero-day attacks.
- Provides workflows and automation capabilities to enable security analysts to investigate incidents, initiate response actions, and generate reports for further analysis and compliance purposes.

SIEM cooperation with other systems
Now let’s look at it in more detail. First, SIEM solutions collect and aggregate security events and data from various sources, such as logs, network traffic, and endpoints. These events are then normalized, enriched, and correlated to identify patterns, anomalies, and potential security incidents. SIEM then links with other security systems such as NDR, EDR/XDR, and UBA to provide a comprehensive view of security incidents occurring in the organization. For example, NDR provides network-level monitoring and threat detection to detect and analyze anomalies in network traffic and identify vulnerabilities in the network infrastructure.
Meanwhile, EDR provides monitoring and protection of endpoints, including desktops, laptops, mobile devices, and servers. It tracks and analyzes device user actions and identifies abnormal behavior and vulnerabilities. Finally, UBA uses user behavior analysis and machine learning to identify unusual behavior users and detect insider threats. SIEM ties all these systems into a single platform that enables full context and analysis of security events and incident management. It uses rules, policies, and algorithms to analyze the data and generate alerts or notifications for suspicious activities or behaviors. As a result, security analysts can investigate these alerts, validate potential security incidents, and take appropriate action to mitigate risks.
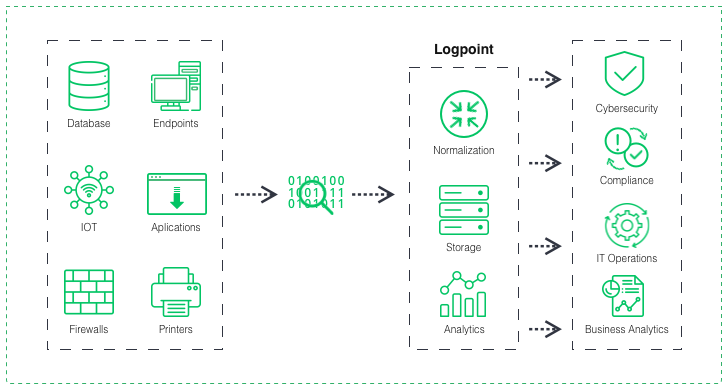
SIEM functions
Benefits of SIEM:
- Provides real-time visibility into security events and data, allowing organizations to detect potential threats early and proactively mitigate risks.
- Automates incident response processes, enabling organizations to respond quickly and effectively to security incidents, minimizing the impact, and reducing response time.
- Helps organizations meet regulatory requirements by monitoring and auditing security events and data to identify non-compliant activities.
- Provides a centralized platform for managing security events and data from multiple sources, simplifying security operations and improving efficiency.
- Generates comprehensive reports and analytics on security events and data, providing organizations with insights for making informed decisions and improving their security posture.
Limitations of SIEM:
Unfortunately, each technology has limitations, and SIEM is no exception. So, these limitations are listed below:
- Complexity: Such solutions can be complex to implement, configure, and manage, requiring skilled personnel and resources.
- Cost: It can be expensive, including upfront costs for hardware, software, and licenses, as well as ongoing operational costs for maintenance and updates.
- False positives: Sometimes SIEM solutions may generate many false positives, requiring security analysts to spend time investigating and validating alerts.
- Scalability: In some cases, handling large volumes of security events and data may face challenges, requiring proper scaling and optimization.
SIEM features and capabilities:
- Collects and aggregates security events and data from various sources, such as logs, network traffic, and endpoints, providing a holistic view of an organization’s IT environment.
- Normalizes and enriches security events and data to provide consistent and meaningful information for analysis and correlation.
- Uses rules, policies, and algorithms to analyze security events and data for identifying patterns, anomalies, and potential security incidents.
- Generates alerts and warnings for suspicious activities or behaviors, enabling security analysts to investigate and respond promptly.
- Automates incident response processes, such as triggering actions, generating tickets, and orchestrating workflows, to streamline and accelerate incident response.
- Generates comprehensive reports and analytics on security events and data, providing insights for improving security operations and decision-making.
Next-Gen SIEM Capabilities:
With the ever-evolving threat landscape, Next-Gen SIEM solutions have emerged to address the limitations of traditional SIEM systems. These advanced SIEM solutions incorporate additional capabilities to provide more effective and efficient threat detection and response. Some of the Next-Gen SIEM capabilities include:
- Leverages machine learning algorithms and advanced analytics techniques to analyze security events and data. This enables more accurate and timely threat detection.
- Incorporates UEBA capabilities that analyze user and entity behavior to detect anomalies and insider threats. UEBA helps identify abnormal behaviors that may indicate compromised accounts or insider attacks.
- Integrates with threat intelligence feeds and databases to provide context and enrichment to security events and data. This helps organizations identify known threat indicators and patterns and stay up-to-date with the latest threat intelligence.
- Extends its capabilities to cloud and IoT environments, allowing organizations to monitor and protect their assets in these complex and dynamic environments.
- Integrates with SOAR platforms to automate incident response workflows. It allows organizations to respond faster and more effectively to security incidents.
- Provides real-time monitoring and response capabilities to spot and respond to threats in real-time. It reduces the time window for potential damage.
- Offers advanced visualization and dashboard capabilities that provide visual representations of security events and data, making it easier for security analysts to identify patterns and trends.
In conclusion, SIEM is a critical cybersecurity technology that helps organizations detect, respond to, and mitigate cyber threats. However, although it provides capabilities described the above, it also has limitations. Next-Gen SIEM solutions have emerged to address these limitations, incorporating advanced capabilities such as machine learning, UEBA, threat intelligence integration, cloud and IoT security, SOAR, real-time monitoring and response, and visualization and dashboards. Therefore, organizations must carefully evaluate their cybersecurity requirements and choose the right SIEM solution, traditional or Next-Gen, to protect their IT environment from advanced cyber threats.