The recent outbreak of Cl0p ransomware touched a number of companies. Among them are not only mediocre organisations but also a number of worldwide-known names. Cl0p boasts of succeeding in all of these crimes using the GoAnywhere vulnerability. But what is that about? And how to protect against that breach?
What is Cl0p ransomware?
Cl0p is ransomware used by several threat actors, most commonly TA505 and FIN11. Its name (clop) in Russian means “bedbug” – and it is somewhat representative of its functionality. To hide from anti-malware software, it uses leaked (“sucked out”) certificates of other, valid programs. Appearing back in 2019, it is considered one of the offsprings of CryptoMix ransomware. Apart from that, Cl0p is known for extorting money not only for data decryption, but also for preventing publishing the of leaked data. Malware starts stealing all the files it can reach even before the encryption. That practice received the name of double extortion.
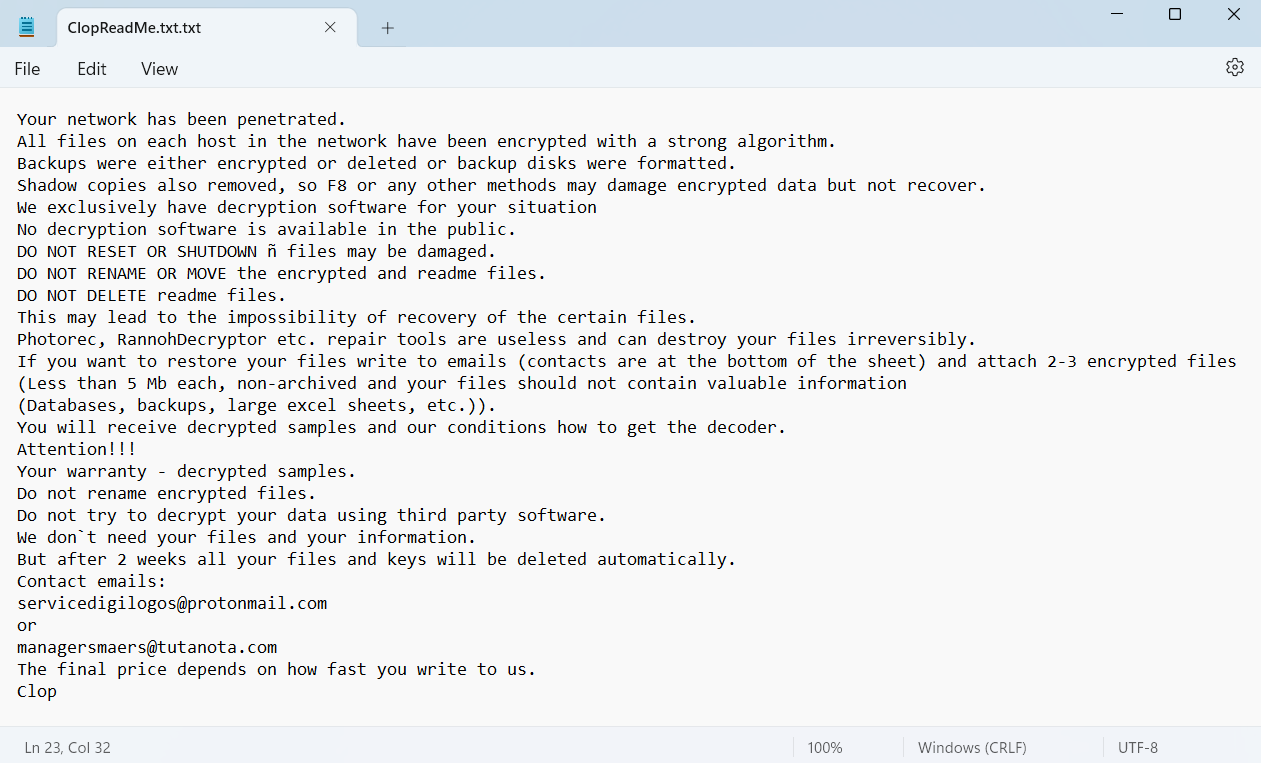
The example of Cl0p ransom note
Being malware that aims generally at corporations, the choice of vulnerabilities as a method for initial access and lateral movement is obvious. Through the years, TA505 managed to deploy Cl0p via breaches in file transfer appliance protocol. Most widely used breaches are CVE-2021-27101, CVE-2021-27102, CVE-2021-27103 and CVE-2021-27104. Aside from that, threat actors do not disdain using droppers and exploit kits, like Amadey, FlawwedAmmy and RIG EK.
What is the GoAnywhere vulnerability?
GoAnywhere is a network file transfer utility used in corporations. It is notable for more complicated security appliances and events logging. But as it turned out, its secureness is not as good as companies used to think it is. CVE-2023-0669 makes it possible to execute any command in the administrator console without authorisation. The breach was tracked since February 6, 2023, but was exploited by Cl0p for at least one month. Through that period, hackers managed to breach over a hundred of companies, including Procter & Gamble, Rio Tinto, Hitachi Energy and a row of other companies.
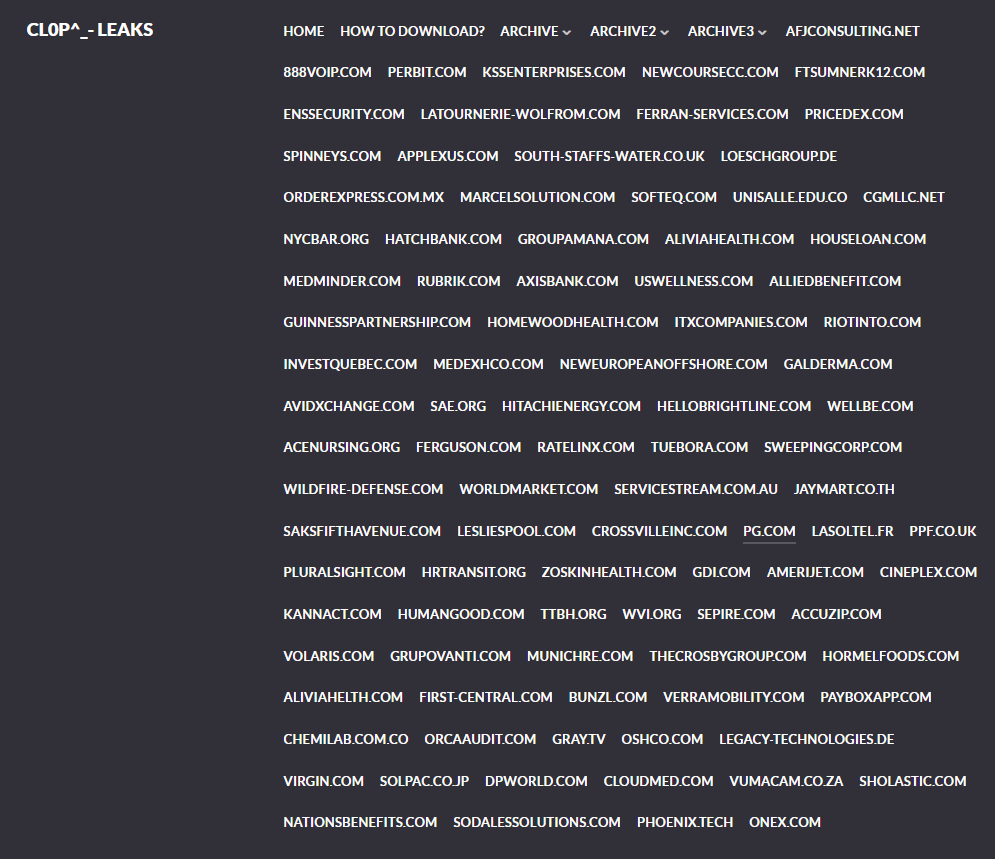
List of companies published on Cl0p leak site
The mentioned breach is present in all versions of the program, except the latest. Fortra, the developer of GoAnywhere, already released a patch. 7.1.2. is known to contain the fix of this vulnerability. Such a fast reaction, however, does not mean that the vulnerability is already beaten. All the companies who use the utility should update it to the latest version as soon as possible.
How to stay protected?
TA505 itself, as well as their beloved Cl0p ransomware, are extremely cunning threats that are pretty hard to avoid. However, some measures will significantly decrease the risk of being listed on the Cl0p leaks site.
Update your software as often as possible. Software vendors release minor updates and offer you to install them not only to annoy or distract you. Most often, they contain fixes for small bugs or overall improvements to the codebase. However, some of them close the security breaches like the one in GoAnywhere. Using outdated software is not dangerous – until there is a hacker group that wants to rob you. And they will appreciate outdated programs that have known vulnerabilities unpatched.
Use zero-trust security solutions. Zero-trust is most probably the only consistently-working response to zero-day vulnerability threats. The very essence of this policy supposes that no programs are trusted, without any exception. Such a radical position is accomplished by a number of check-ups done on every file and program you launch. For sure, that requires more computational power – but it is a completely new level of security that is worth it.