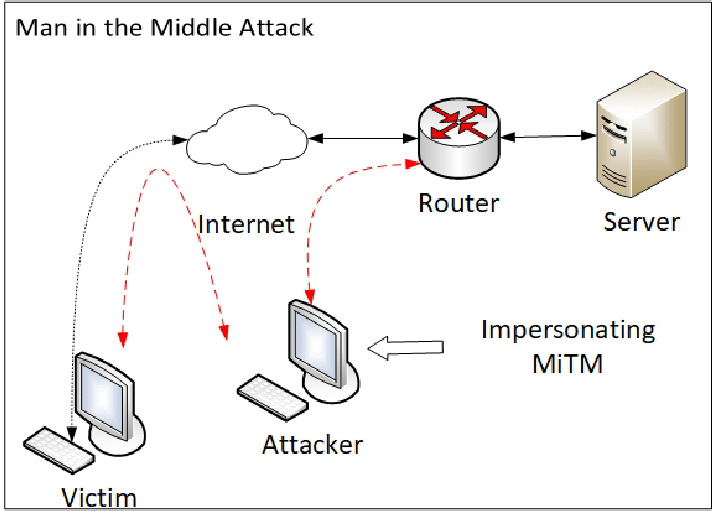
Man-in-the-Middle attack is a cyberattack where threat actors get hold of communication channels and can interfere with them. No one from the participating party will know that there’s someone third in the channel. Sometimes this type of cyber threat is called man-in-the-browser, monkey-in-the-middle, machine-in-the-middle, and monster-in-the-middle. An attack may happen through different channels, primarily the infected router or malicious proxy servers. The attack usually begins with the use of malware that victims receive via phishing emails.
With this attack, threat actors aim to steal various information. Their usual point of interest is credit card numbers, login credentials, personal details, etc. The attack occurs in real-time and may continue until the victim uses the connection.
How Does MitM Attack Work?
The key point of a MitM attack is to get into the connection between the client and server. In some cases, hackers may impose the server by spoofing the page the user tries to connect to. For that trick, hackers use DNS spoofing tactics. But more often, things end up spoofing the client and server’s public key to ensure the connection’s secureness. Then, they receive all the packets from the client-server communication. The used encryption is not a problem, as crooks send the spoofed key to both parties.
MitM attack step-by-step
In the first step, threat actors intercept data transferred between a client and a server. Both are tricked into believing they have a secure and genuine connection, while threat actors work as a proxy in communication. This step allows them to read and inject false information into the compromised channel. There could be certain variations, depending on the way the hackers perform the MitM attack:
- Router is under threat actors’ control. That allows the crooks to control all the traffic that passes through. This action certainly requires some the use of software or a specific firmware on the router. However, crooks will have one if they launch a Man-in-the-Middle attack.
- Crooks control the victim’s DNS record. Such a situation may happen because of the router hack or the malware injection into the victim’s machine. Either way, hackers may redirect the victim to the fake version of the target site. All they need is to spoof the corresponding DNS record. As you can suppose, crooks can easily access all the traffic to and from the site.
- Hackers intercepted the connection between client and server. In that case, they took over the connection to the legit page. The client and server receive the security key that hackers generated, especially for that purpose. With that spoofed key, they can decrypt the data packages. This practice requires the site that lacks the additional security checkups that can prevent the forged key injection.
 Is a real RED light for the different kinds of spyware
Is a real RED light for the different kinds of spyware
There could be different alterations and conjunctions of these methods. Depending on the situation, hackers can change how they break into the connection.
What Are The Main Types Of Man-in-the-Middle Attack
To get access to the victim’s device and sensitive information, threat actors will make a Man-in-the-Middle attack in one of the following ways:
- Cache Poisoning. Specialists also name it Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) cache poisoning. This is one of the most popular modern-day MiTM attacks. It allows threat actors to reside on the same subnet as the victim to eavesdropping on all traffic on both sides;
- Session Hijacking. In another way it is called stolen browser cookies MiTM attack. Threat actors hack browsers, stealing valuable information in cookies. With this kind of an attack, crooks can gain an immense source of various valuable information to get their hands on;
- Wi-Fi Eavesdropping. This kind of Man-in-the-Middle attack threatens those who use public Wi-Fi networks. During the Man-in-the-Middle attack, hackers create Wi-Fi hotspots that have names resembling local shops, restaurants, cafés, etc. With such a trick, unsuspecting users connect to a malicious hotspot. Then, attackers can access to victim’s online sessions;
- Email Hijacking. This is where threat actors get control over a victim’s email account. They usually aim at the one you use for banking or other financial activity. In that way, rascals can view all the transactions done. Sometimes threat actors can make a spoof a bank email address to send to its customer’s fake notifications and luring them into transferring money to threat actors;
- Secure Sockets Layer Hijacking. When a web server and client establish a secure connection, they rely upon SSL protocol. Threat actors compromise this protocol with the help of another computer and another secure server. Then hackers intercept all the information that goes in and out;
- HTTPS Spoofing. HTTPS means having a secure and safe Internet connection, while HTTP means no security. In an HTTPS spoofing attack, crooks redirect the victim’s session to an unsecured connection without the user suspecting this. In such a stealthy way, threat actors can view any victim’s interactions and see any shared information;
- Domain Name System Spoofing. When doing DNS spoofing, threat actors change domain names and reroute users to fake websites. Instead of landing on some legitimate website, users will end up on a website the threat actors have full control of. The main aim of this attack is to redirect traffic on the threat actor’s website or steal login credentials;
- Internet Protocol Spoofing. Here, threat actors change the source IP address of a device, email or website to make victims believe they are dealing with natural resources. Instead, they will give up all their important information to criminals.
How To Prevent Man-in-the-Middle Attack
Usually, in any cyber threat, the best solution will be the proactive one. A few steps can be followed to ensure defense against this cyber threat:
- Using VPN. VPN tool encrypts your connection and transmits online data, so even if threat actors manage to get a hold of your channel, they won’t be able to decipher it. The encryption VPN offers will protect your valuable information like passwords or credit card information. This functionality of VPN may be useful not only to ordinary users. Organizations must ensure their employees access the company’s workspace with a secure connection. It became especially important when remote working became way more popular;
- Being cautious against phishing emails. One of the major precursors for all kinds of attacks is phishing. It aims at forcing the victim to start the attack. Be cautious when receiving any emails that try to mimic the one from your bank asking you to update your login.
Please don’t click on any links in such emails, as they might redirect you to some malicious website or trick you into installing malware. Think twice before opening or clicking correspondence that comes from unknown or unverified sources;
- Using secure connection.Surfing on the internet, you better look for websites with HTTPS connection and padlock in a search bar. They mean that the connection is secured and safe; your valuable and important information won’t get stolen.
Also, try not to use public wifi networks as they often don’t offer complete security and easily get hacked. In organizations, multi-factor authentication should be put in place across the board to ensure an additional layer of online security; - Educating users.Most cyber-attacks occur because of human error. Employees should be acknowledged on how to recognize malicious emails, what are the best security practices and why it’s not advisable to use public wifi networks;
- Implement endpoint security.Having antimalware and internet security products on board is no less important because MiTM attacks also execute malware. You can prevent the spread of malware by having effective tools present on your system.