IP sniffing or packet sniffing is a practice that network administrators use to monitor and analyze a network they are in charge of. Packet sniffing allows gathering, collecting, and logging certain or all network packets going in and out. Network administrators use sniffing practices for various administrative purposes like monitoring traffic and bandwidth. IP sniffing practice is also known as protocol analyzing, network analyzing, and packet sniffing.
In addition to monitoring the network administrators can also with the help of this practice troubleshoot network-related problems. Usually, monitoring networks via IP sniffing takes place over TCP/IP networks. Not only network administrators but hackers of all kinds make use of the IP sniffing practice. Exploiting the IP sniffing method gives threat actors a clear view of not only the state of a given network but also its vulnerabilities.
How IP Sniffing Works
To do IP sniffing, network administrators need two main components: network adapter and software. A network adapter acts as a basis for connecting a special tool — a sniffer. It looks like a tiny plug-in device; it can be attachable to the router motherboard. Sniffing software, on the other hand, supposes the changes to the router’s firmware. In any case, the sniffer stores the collected packages in the log files. Then, the administrator examines these logs to find the information it needs. To understand how IP sniffing works first you need to understand how networks actually work.
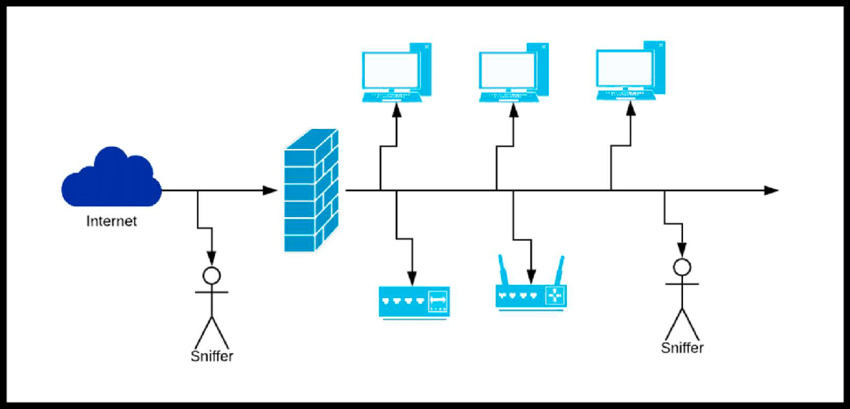
Visualization on how generally packet sniffing works
A network consists of nodes – servers, personal computers and networking hardware connected and thus forming a network. The existing network connection makes it possible for the data to be easily transmitted between devices connected to it.
These connections can be physical, wireless or be a combination of both. Each node sends and receives data which comes in the form of a packet. For each packet type, there’s a specific length and shape. These parameters allow checking data packets for their completeness and usability. And because of the constant data transmission, each node has to differentiate whether this or that particular data packet is going to the right destination. The assignment of specific addresses to each transmitted data packet helps with the task. Under normal circumstances, each node can reject a data packet if it has the wrong direction but a packet sniffer will collect any data packet.
What Are The Types Of Packet Sniffers
There are two main types of packet sniffers:
- Software Packet Sniffers. That is the mostly used tool these days. Unlike any network interface that can capture only bits of data transmitted it can be configured to capture all traffic going through the network and present the results of its work to network administrators;
- Hardware Packet Sniffers. A physical packet sniffer that needs to be installed directly onto the network. The physical packet sniffer is more useful because it can ensure that all transmitted data will be collected and stored for further analysis.
Due to filtering, routing, or other inadvertent and deliberate reasons some data packets can simply get lost to software packet sniffers but hardware packet sniffers capture them all.
But to capture all data on an entire network administrators will need to use multiple packet sniffers because packet sniffers can only capture data that is received on the specific side of a switch or router. On each network segment administrators need to provide one packet sniffer.
What Data IP Sniffing Allows To Capture
IP sniffing brings an important notion of cybersecurity up front. Any threat actors exploiting the IP sniffing tools for their own purposes can get access to some really valuable and sensitive information. For example, if someone uses IP sniffing for bad purposes IP sniffing they can view an HTML and CSS of a webpage a victim visits. Not to mention that in such a way threat actors can get to see your passwords and usernames because they will have access to all the transmitted data packets.
One of the solutions against malicious IP sniffing can be using VPN service that will encrypt your transmitted data and scramble it so that anyone who would intercept it won’t be able to read it.
What Is Sniffing Attack
Even though the primary use of IP sniffing is quite legitimate to monitor and analyze the network by network administrators, there’s little in the IT field that has not been exploited by various threat actors. Threat actors can exploit IP sniffing methods to capture different kinds of information like passwords, usernames, customer data and to compromise the security of a targeted network.
With an IP sniffing mechanism threat actors can conduct other cyber attacks like Man-in-the-Middle attack, insider threats, etc.
How To Prevent Sniffing Attacks
If you’re concerned over your network safety you can use several preventive measures against future network breaches:
- Enable regular network scanning and monitoring. One of the things users and network administrators can secure and protect their networks from unauthorized access. Ethical hackers can help to detect where on the network can data breaches happen, and offer risk mitigation ways. In addition, the regular analysis and monitoring of the network can help detect any present network security breach in time;
- Use VPN. VPN tools offer users the much-needed encryption of any data they would transmit via an insecure connection.
VPN adds its cipher to your data, so any third party that can theoretically get the packets won’t be able to read it. Usually that’s the public wifis that pose the most danger concerning the safety of networks so use a VPN anytime you need to hop onto public wifi network; - Try to avoid unsecured networks. Usually public wifis can have unsecured network connections and that’s what threat actors actively try to exploit with Man-in-the-Middle attacks, for example. If you urgently need to do some transaction on a website it would be better to use mobile internet than using some public wifi hotspot.