In 2021, the cryptocurrency market grew from less than $200 billion to nearly $3 trillion, attracting new crypto investors. However, it all collapsed in the first half of 2022. While the cryptocurrency market is still worth about $900 billion, the risks to investors have multiplied over the past few months. That’s why investors need to do their due diligence and understand what they’re investing in. So, if you are interested in cryptocurrency, you need to know how to invest wisely in your crypto investments.
What Is Cryptocurrency?
Cryptocurrency is a digital currency you can theoretically use to buy goods and services. However, it is more often bought and sold as an investment or used to implement decentralized finance (DeFi) software projects on various blockchains. Created back in 2009, Bitcoin was the first cryptocurrency. Since its inception, the number of coins has grown to more than 19,000. Although Satoshi Nakamoto created bitcoin for digital payments, investors have seen it more as a means of savings than a practical digital currency. It is also referred to as a form of “digital gold”.
Despite the sophisticated encryption and privacy features used to protect user anonymity, any cryptocurrency can hardly guarantee complete anonymity because most blockchain transactions are recorded and accessible in a public registry. Consequently, since the blockchain registry is available for everyone, maintaining anonymity is difficult, especially in the case of Bitcoins. Generally, Bitcoin is pseudo-anonymous because it is possible to find the relations between a person and a certain Bitcoin address. Still, it will not be a real name or home address. You may as well know that the address is associated with a single person, but you don’t know who exactly. Consequently, Bitcoin, like most cryptocurrencies, is not entirely anonymous.
What Is Blockchain?
Blockchain networks power cryptocurrencies. A blockchain is a digital register that consists of expanding blocks of data. Because of the blockchain’s distributed ledger, multiple computers in the network keep the records. Each computer called a node; these nodes check and store the data. Each new transaction is added to a “block” of data, and then that block is added to the chain. This transaction updates the whole book, so all the nodes will receive the information. Many crypto-enthusiasts say that blockchain technology could be the basis for the next evolution of the Internet a.k.a Web 3.0. You can use blockchain technology for games, finance, and other purposes. And to make transactions, you need to be able to pay the appropriate fee in the proper cryptocurrency.
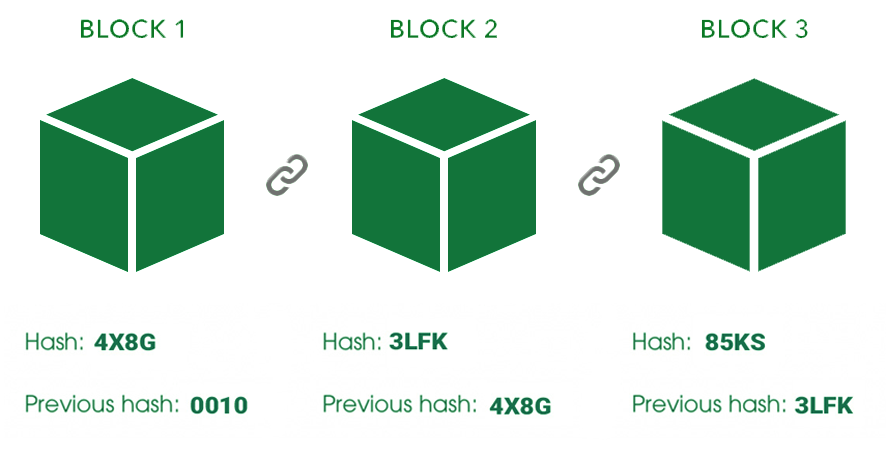
Determining the value of a cryptocurrency
Several factors determine the value of a cryptocurrency. Although with so many cryptocurrencies, it can be challenging to decide which ones are precious, like many other assets, one of the main factors affecting the value of a cryptocurrency is demand. The more people use a particular coin or blockchain associated with a coin, the more likely the price will rise. Most people use well-established cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin and Ethereum, which have a higher value than other cryptocurrencies. Some experts point to the first-mover advantage that these two cryptocurrencies have. Actually, at this logic cryptos repeat “classic”, government-backed currencies a.k.a fiat money.
Also, the supply may influence the price or investors’ perception of its value. For example, many experts believe that Bitcoin will likely retain its value because there is a limit of 21 million Bitcoins. So it is likely that scarcity contributes to its weight, unlike cryptocurrencies which have no quantity limit. When considering which cryptocurrencies to invest in, it is helpful to look at coins with a reliable use case and a greater likelihood of broader adoption. For example, Ethereum is considered valuable and second only to Bitcoin because its intelligent contracting capabilities allow for several applications, including finance and gaming.
How Can I Use Cryptocurrency?
You can use cryptocurrencies to buy things in the real world, but it doesn’t make sense for most people. The volatility and unstable value of cryptocurrency mean that the price you pay today could be much higher or lower tomorrow. As mentioned above, in addition to using cryptocurrency as an investment, you can also use it to gain access to blockchain networks such as Ethereum and other networks that allow developers to create software. In addition, different apps offer linking crypto debit and credit cards to exchange accounts, allowing you to integrate actual purchases into your crypto portfolio. PayPal, for example, gives the ability to use cryptocurrency to pay online. But so far, crypto is more and more often sees use as an object of investment. For instance, a couple of large U.S. insurance companies offered retirement and life insurance plans that include crypto investments.

How Is Cryptocurrency Mined?
Cryptocurrency mining is a process that uses the computing power of a device to validate transactions on a blockchain. In this way, miners provide the resources of their devices to perform transactions. However, those who solve cryptographic puzzles and perform other computational work receive their reward with more cryptocurrency. Over the years, cryptocurrency mining has become increasingly sophisticated and competitive. As a result, many miners build or buy specialized expensive equipment to provide the computing power needed in an increasingly competitive environment. However, this does not assure that you will get proper rewards for mining. Environmental issues are also associated with cryptocurrency mining, as the equipment consumes great amounts of electricity to mine.

How to Store Cryptocurrencies?
There are different ways to store cryptocurrency. Many cryptocurrency exchanges allow you to keep your coins on an exchange. However, they may then be vulnerable to hacking, and the exact marketplace may charge a fee for keeping the open position overnight. While some businesses have insurance to mitigate losses, it is essential to note that cryptocurrency investments do not have same federal protections and guarantees, as a typical stock portfolio has. The safest way to store cryptocurrency is through a crypto wallet. There are two main types of wallets:
- Hot wallets. You can find them in different apps that pose as crypto infrastructure. It is possible to access them and connect to various online exchanges. In addition, you can quickly send your cryptocurrency from a business to a hot wallet by keeping them separate. The other name for hot wallets is software wallets.
- Cold wallets. Unlike hot wallets, they generally appear as physical carrier, which contains all the needed information. As a result, cold wallets are more expensive than hot ones. However, they are considered more secure, as the key source of danger – the Internet – is absent. But it also means that if you lose or break the cold wallet, you lose your cryptocurrency forever, with no chance to recover it.
Cold Wallet vs. Hot Wallet – Which is Best?
When choosing between a hot or cold wallet, it is essential to understand the risks associated with each. A hot wallet usually includes an option to recover lost keys. You can use them as another account with a password. If you have the right passphrases, you can often regain access to it. However, you must be prepared to take security risks. With a cold wallet, it may not be as easy for you to recover. If you lose or forget the keys needed to access the wallet, you may not be able to access your crypto assets. In addition, you could also lose your assets if the hardware wallet is destroyed without a backup.
When storing your cryptocurrency, it is essential to determine a system that works for you. For trading, keeping your coins on an exchange may make sense. However, you may also need a hot wallet for online transactions and moving your cryptocurrencies. For long-term storage, a cold wallet is best, as experts recommend cold wallets for maximum security. You can also use a combination of storage options to get the results you want.
Cryptocurrency and cybersecurity
After several European countries implemented stricter anti-money-laundering measures, allowing more detailed monitoring of bank transfer transactions, the era of crimeware subsided for a while. But with the advent of cryptocurrency, cybercriminals who managed adware, traffic arbitering, and ransomware, got their second chance. The decentralization of cryptocurrency opens vast opportunities for cybercriminals. Moreover, the anonymity of some cryptowallet services and exchanges allows them to act with minimum traces. This way, cybercriminals can hide their real identity by demanding a ransom in digital currency. Still, there are enough ways of getting some valuable facts about threat actors – as practice shows, the authority of the FBI and Europol is sometimes enough to make “anonymous” services way less anonymous.
These days, cryptocurrency is the favourite way of payment for any malware attacks. Although Bitcoin is the most expensive cryptocurrency, Monero, and Litecoin are more popular among cybercriminals. Transaction speed is a definitive factor for a lot of operations, and ransom payments are not an exclusion. While a money transfer in BTC will be delivered in about a day, LTC/XMR transactions last less than an hour. Such properties of alternative cryptos also open the door for different disguise tactics. Some methods include hiding a user’s natural balance and wallet address through cryptomixers. After these manipulations, they can convert cryptocurrencies into fiat money without any risk. These days, crooks can also hack into cryptotrading platforms and steal funds – a common threat for hot wallets we’ve described above. But a much more common type of cryptostealing bears upon scam giveaways, and cryptostealing malware that aims at users’ wallets.
CPU mining
Monero, as well as Litecoin, are the point of crooks’ interest not only because of their transaction speed. The other type of cybercrimes aims at exploiting someone’s hardware to mine cryptocurrencies. Coin mining malware saw its first boom simultaneously with the crypto rush of 2017. BTC price peaked at $20,000, and a lot of alternative tokens popped out. LTC, XMR, an infamous Ripple and many others appeared as a substitution for Bitcoin in daily payments. They use a way less complicated encryption and smaller block size, which makes the mining less resource intensive and fast enough to serve for small transactions, like shopping or energy bills. In these circumstances, hackers decided to use the processors of infected PCs for mining – even though GPUs are way more effective at that purpose. That is the source of another name of this malware – CPU miners.