Windows is an epoch-making operating system. It has a monopolistic position on the personal computer systems market. To make the system more comfortable for different categories of users, Microsoft created a lot of embedded services. Their purpose is to improve the experience of OS usage. However, these services are unnecessary for many users and can slow down outdated systems.
Sometimes, even powerful systems may suffer from lags because of these embedded applications. It becomes a straightforward rule once we are talking about systems that use HDD as a system disk. Besides Windows-caused troubles, your PC may be slowed down because of trivial hardware problems, which don’t depend on the software you use. To prevent these problems, it is recommended to know the hints that can make your system faster without any functionality loss.
Explaining the reasons
Windows tries to be an all-in-one system, that can be understood by everyone and fit all possible needs. However, it is pretty hard to satisfy all of these parameters. Microsoft created the services to make the different device’s connection much easier. Of course, to make these services faster and more efficient, it must be running together with Windows, without the ability to be disabled from launching. For example, that is a separate service for printer connecting. After the new device is connected, it tries to find its latest drivers. But what if you do not use any printers, scanners, graphic pads, and so on?
Windows does not give you the ability to choose. It will start all these services until you do not forbid their launching manually. The problem is that you will not find a separate menu in the Settings, where you can disable all services you don’t need. It is done to prevent the changes that can lead to system malfunctioning. To make the changes, you need to dig deeply into the system configuration settings, which are located in the Group Policies, Services menu and in registry.
Some shallow changes may be done without dealing with the deep system settings. However, these changes are often not enough.
Let’s optimize it
First, let’s check the optimization tricks that require neither registry nor Services list editing.
Disable the excessive startup apps and app relaunch.
It can be easily understood why the startup is needed, but who needs the ability to restore the programs used at the moment of reboot? You will barely be able to restore the data you lost in such a way, but if the app is capable of its own data restoration, you will be able to do it even without Windows help.
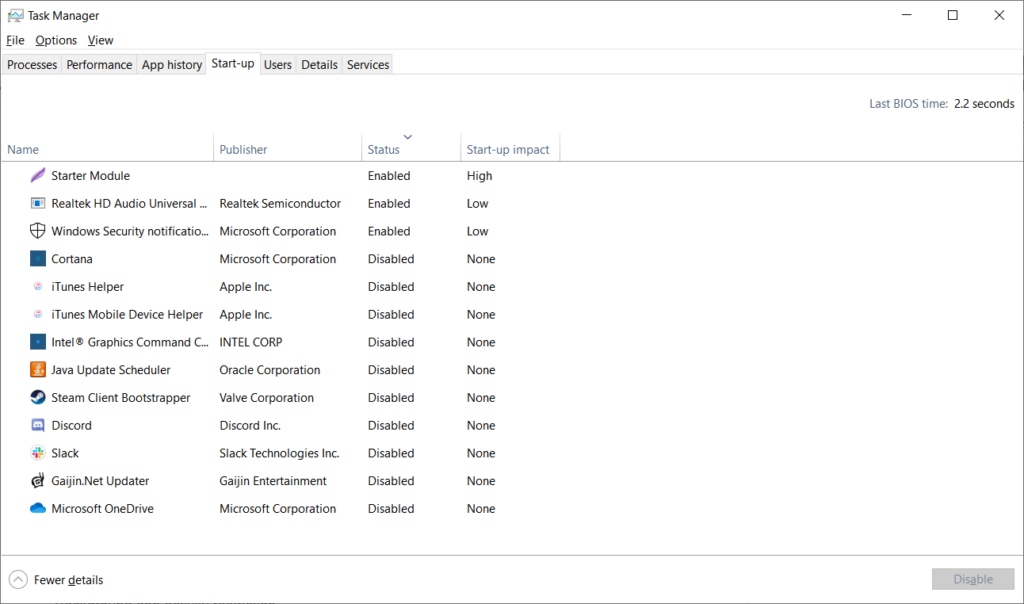
Open Task Manager, then go to the Startup tab. Here you can see all apps which are starting together with Windows launch. Disable the apps which you don’t need to use immediately after the system launch. But be careful: such apps as Realtek HD Audio Universal service are needed to be run with Windows start because it is responsible for correct sound processing.
Background app activity restriction
Apps that are running in the background may consume a large amount of CPU and RAM. In spite of several Windows features which oppress the app consumption after its window has been minimised, the troubles can still appear. If you have a massive amount of background-running programs, they can make the described feature totally useless.
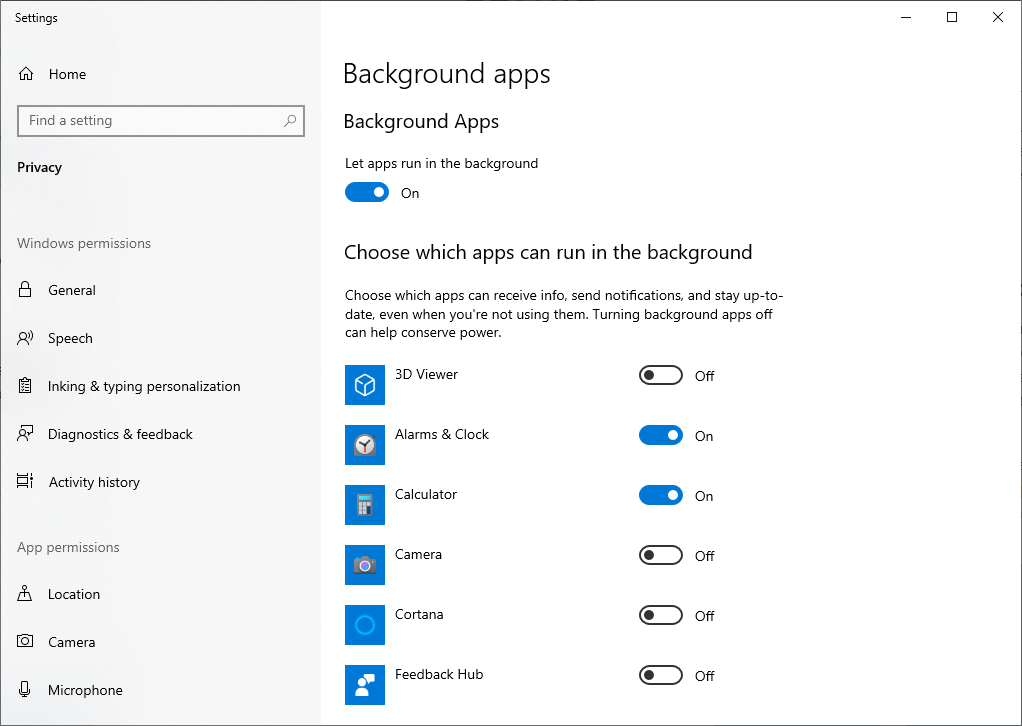
Open Settings → Privacy → Background apps. Here is the list of the programs which are allowed to run in the background. Such proprietary applications as Feedback Hub, Maps, Solitaire, Microsoft Store, Weather and many others may be disabled without any doubt – their functionality wouldn’t change after that.
Keep your disk drive clean
Disk drive(s) may be used by the system to create so-called dump files for the applications which are unloaded from the RAM, but still running in the background. The size of this dump may vary, depending on the size of the unloaded app and the total amount of your random-access memory. It is recommended to have the amount of free space on the disk that is equal (or close) to the amount of your RAM.
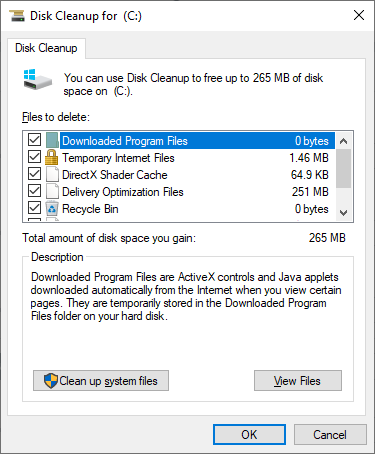
You can perform the disc cleaning using a Windows proprietary tool called Disk Cleanup. It is capable of cleaning any disks plugged into your PC. Open Control Panel → Administrative Tools → Disk Cleanup, then choose the disk you want to clean up. If the amount of memory that can be freed up is not enough, press the “Clean system files” button. This allows you to delete old updates and update logs that can take up to 10 gigabytes of your disk space.
Use defragmentation tool (HDD-based systems only)
The specificity of hard disk drive technology supposes that there can be a situation where the files of the program you use can be stored in the different physical areas of the hard drive. So, when the system/app requires a file located on the other side of the HDD, you need to wait until the hard drive’s read/write heads reach this region. It takes less than a second for one file, but imagine if you have all files scattered throughout the physical areas of the HDD. Defragmentation procedure can be performed with standard Windows tools.
Open Control Panel → Administrative tools → Defragment and optimize drives. This utility usually tracks the disk health constantly, so even if you have never used it, you will see the current defragmentation ratio of your HDD.
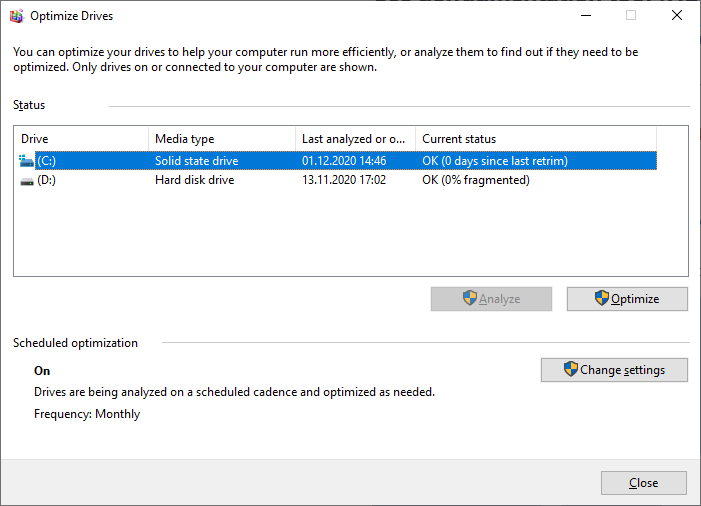
IMPORTANT: do not perform the defragmentation operation with SSD! It is useless for them because of other data storage techniques and may lead to increased solid-state drive deterioration.
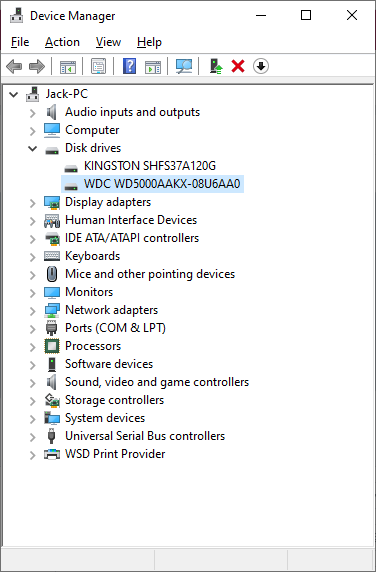
Update the drivers of your storage devices
Storage devices may get the updates which may increase their performance significantly, especially when we are talking about large (2TB+) disks.
Open Control Panel → Hardware and Sound → Device Manager. Your storage devices are listed under the Disk Drives tab. Now, when you know the exact name of your storage devices, search in google for the drivers for them. The driver installation instructions are usually available on the website you are downloading these drivers from.
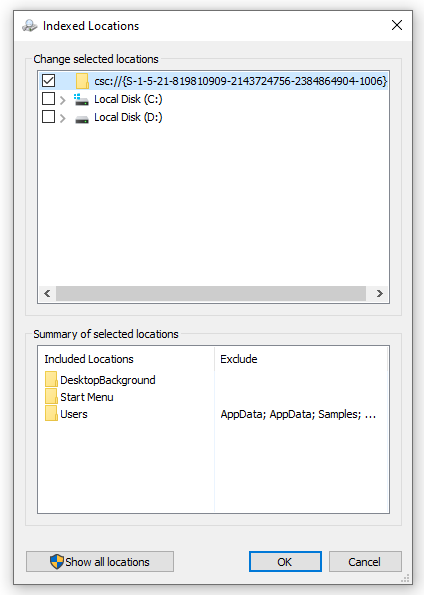
Disable search indexing
Indexing is created to make the file search much faster. However, searching by files in Windows works awfully, regardless of the indexing, so no one uses it. At the same time, the majority of users know where their files are stored, so there is literally no need in this function.
Open Settings → Search → Searching Windows, then click Advanced Search Indexer Settings. In the appeared menu, click “Modify”, then “Show all locations” and take away the marks in front of all the folders/disks. Search indexing will keep going, but it will no longer index the directories you unmarked, unloading your CPU from useless work.
Deep-system Windows tricks
As it was mentioned, you need to edit your registry and services. To do it, press Win+Rto open the Run system app, then type “regedit” for registry editor.
Unregistered registry
Check the following registry hives/keys:
HKEY_CURRENT_USER/Software
Check this hive for the programs names you have already uninstalled. The keys created by these applications are still checked by Windows, regardless of their presence. Delete the hives that refer to the deleted programs.
HKEY_CURRENT_USER/Software/Microsoft/Windows/CurrentVersion/Run.
HKEY_CURRENT_USER/Software/Microsoft/Windows/CurrentVersion/RunOnce.
These hives contain information about startup programs. Some apps may not be displayed in the startup menu, so it is better to check this out and disable it if you don’t need to use them immediately after the system launch.
It is likely all places in the registry can be cleaned without harming the system and on most machines. Other changes are purely individual or can be dangerous for your system stability, and that’s why they are not recommended to be implemented.
Services, services, services
Windows has tens of services that usually run in the background, regardless of the need for these services. Most laptops/desktops do not have touch keyboards, scanners, or directories in common access. However, Microsoft thinks that usage or non-usage is not essential, so weak systems are just choking with these services, which are consuming a significant amount of RAM, and making the usage of any other apps impossible. You may disable at least 10% of these services without any losses in functionality, and even up to 20% if you have no periphery and use powerful antivirus tools.
To open the services editing panel, press “Win+R”, then type “services.msc” to open the Windows Services editor. To disable the service, click with the right mouse button on it, then choose Properties, then click on the drop-down list in front of “Startup type” line, and choose “Disable” value.
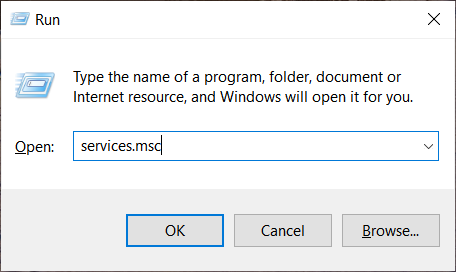
Payments and NFC/SE Manager
Manages payments and Near Field Communication (NFC) based secure elements. It was created for mobile devices running Windows 10, but no one will install the Windows on the phone being sane.
Samsung Network Fax Server
Implements execution of extra features of Samsung fax printer driver. If you don’t use Samsung faxes/printers, disable it without any doubt.
Remote Registry service
Allows to implement the changes to registry from another computer. Can be disabled without any further troubles in 99.5% of cases, especially if you want to increase the security level of your PC.
Windows Error reporting service
Useless service, that must help you to get the feedback for the troubles with your system. It is much faster and easier to search for the solutions on the Internet.
Parental Controls service
This service is a rudimentary thing from Windows Vista. Even if you use Parental Control on your PC, disabling of this service will not inflate the performance of this mechanism.
IPSec policy agent service
Used only with Internet Explorer, and called to check the authenticity of the established secure connection. Disable it, if you use other browsers.
KtmRm for Distributed Transaction Coordinator service
Not needed for the majority of users. If you have any doubts – you may switch the startup type to Manual.
IP helper service
Not used in solitary computers. If you think you may be needed for the home network – switch the startup type to manual mode.
Secondary logon service
Used to launch the process from the other user. It can be needed for programmers (to test the application on the standard user account, for example). Disable it if you are not developing any programs.
Fax service
Fax is a hybrid of landline phones and printers. Used extremely rarely nowadays, you can disable it without thinking.
Windows Defender service
If you have a good anti-malware program onboard, like Loaris Trojan Killer, you may disable Defender. The interesting moment is that Microsoft states that Defender must be disabled automatically after the installation of another security tool, but it doesn’t.
Smart card service
Smart cards are the same rudimentary thing as faxes. Disable it.
Computer browser service
May be useful for system administrators to search for the computers in the network they have established. Disable it, if you are not a system administrator.
Server service
You may disable this service if you are not going to include your computer to the network.
Bluetooth Support service
Useful service that is used on laptops (most of them have the Bluetooth chip on board), but useless for PCs which usually have no Bluetooth.
Windows is not always guilty
 Is a real RED light for the different kinds of spyware
Is a real RED light for the different kinds of spyware
Besides slowness because of the embedded services, your Windows can also be slow because of different viruses onboard. The biggest influence on the PC performance is against adware and coin miners. These types of malware are impossible to wipe out manually, so I recommend you to use Loaris Trojan Remover to check if your computer is infected. If it is, Loaris will surely wipe out all malicious items you have in your system.
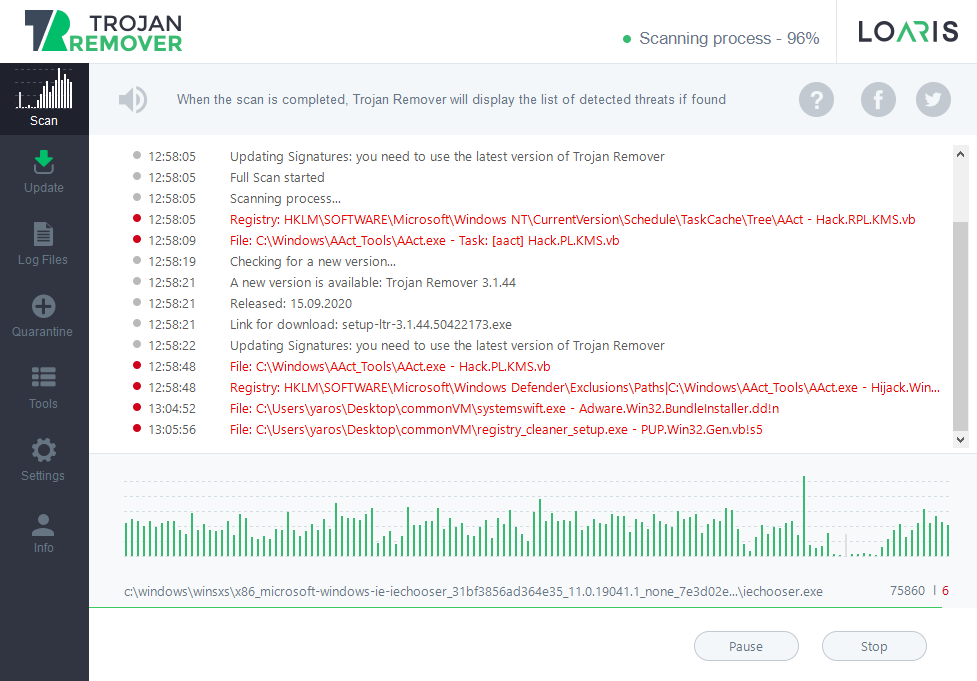
Finally, a site that actually explained what this service “Payments and NFC/SE Manager” does.